ConcurrentLinkedQueue是一个线程安全的队列,它采用的是 CAS 算法来进行实现,也就是说它是非阻塞的;队列中的元素按照 FIFO(先进先出)的原则对元素进行排列,此外,它是一个无界队列;添加元素的时候,在链表的尾部进行添加,获取元素的时候,从链表的头部获取。它内部采用的单向链表的形式来表示,链表的节点是定义在ConcurrentLinkedQueue的一个内部类。
带着问题去理解
要想用线程安全的队列有哪些选择? Vector,Collections.synchronizedList(List<T> list), ConcurrentLinkedQueue等
ConcurrentLinkedQueue实现的数据结构?
ConcurrentLinkedQueue底层原理? 全程无锁(CAS) ConcurrentLinkedQueue的核心方法有哪些?
offer(),poll(),peek(),isEmpty()等队列常用方法 说说ConcurrentLinkedQueue的HOPS(延迟更新的策略)的设计?
ConcurrentLinkedQueue适合什么样的使用场景?
ConcurrentLinkedQueue数据结构
通过源码分析可知,ConcurrentLinkedQueue的数据结构与LinkedBlockingQueue的数据结构相同,都是使用的链表结构.ConcurrentLinkedQueue的数据结构如下:
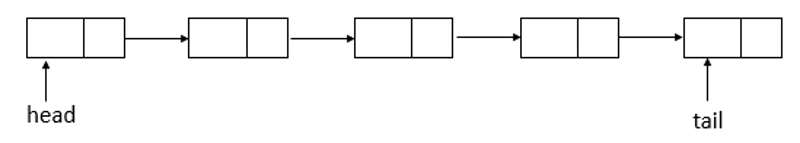
说明:ConcurrentLinkedQueue采用的链表结构,并且包含有一个头节点和一个尾节点.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue源码分析
首先看一下队列中链表节点的定义,链表中的节点使用一个Node内部类表示:
private static class Node<E> {
// 元素
volatile E item;
// next域
volatile Node<E> next;
/**
* Constructs a new node. Uses relaxed write because item can
* only be seen after publication via casNext.
*/
// 构造函数
Node(E item) {
// 设置item的值
UNSAFE.putObject(this, itemOffset, item);
}
// 比较并替换item值
boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val);
}
void lazySetNext(Node<E> val) {
// 设置next域的值,并不会保证修改对其他线程立即可见
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, val);
}
// 比较并替换next域的值
boolean casNext(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
// 反射机制
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
// item域的偏移量
private static final long itemOffset;
// next域的偏移量
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = Node.class;
itemOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("item"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}说明:Node类表示链表节点,用于存放元素,包含item域和next域,item域表示元素,next域表示下一个节点,其利用反射机制和CAS机制来更新item域和next域,保证原子性.
接下来看一下ConcurrentLinkedQueue类中的属性和方法:
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements Queue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
// 版本序列号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 196745693267521676L;
// 反射机制
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
// head域的偏移量
private static final long headOffset;
// tail域的偏移量
private static final long tailOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = ConcurrentLinkedQueue.class;
headOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("tail"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
// 头结点
private transient volatile Node<E> head;
// 尾结点
private transient volatile Node<E> tail;
}说明:属性中包含了head域和tail域,表示链表的头节点和尾节点,同事,ConcurrentLinkedQueue也使用了反射机制和CAS机制来更新头节点和尾节点,保证原子性.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue的构造函数
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {
//初始化头节点与尾节点
head = tail = new Node<E>(null);
}说明:该构造函数用于创建一个最初为空的ConcurrentLinkedQueue,头节点与尾节点指向同一个节点,该节点的item域为null,next域也为null.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E>)构造函数
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Node<E> h = null, t = null;
for (E e : c) { // 遍历c集合
// 保证元素不为空
checkNotNull(e);
// 新生一个结点
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
if (h == null) // 头结点为null
// 赋值头结点与尾结点
h = t = newNode;
else {
// 直接头结点的next域
t.lazySetNext(newNode);
// 重新赋值头结点
t = newNode;
}
}
if (h == null) // 头结点为null
// 新生头结点与尾结点
h = t = new Node<E>(null);
// 赋值头结点
head = h;
// 赋值尾结点
tail = t;
}说明: 该构造函数用于创建一个最初包含给定 collection 元素的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue,按照此 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序来添加元素。
核心函数分析
offer函数
public boolean offer(E e) {
// 元素不为null
checkNotNull(e);
// 新生一个结点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) { // 无限循环
// q为p结点的下一个结点
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) { // q结点为null
// p is last node
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) { // 比较并进行替换p结点的next域
// Successful CAS is the linearization point
// for e to become an element of this queue,
// and for newNode to become "live".
if (p != t) // p不等于t结点,不一致 // hop two nodes at a time
// 比较并替换尾结点
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
// 返回
return true;
}
// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
}
else if (p == q) // p结点等于q结点
// We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it
// will also be off-list, in which case we need to
// jump to head, from which all live nodes are always
// reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet.
// 原来的尾结点与现在的尾结点是否相等,若相等,则p赋值为head,否则,赋值为现在的尾结点
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
// Check for tail updates after two hops.
// 重新赋值p结点
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}说明: offer函数用于将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。下面模拟offer函数的操作,队列状态的变化(假设单线程添加元素,连续添加10、20两个元素)。
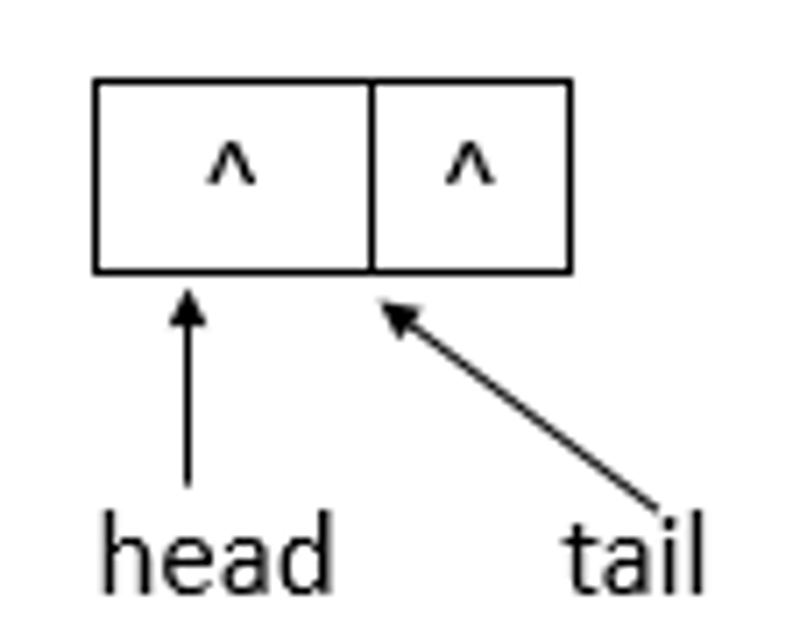
若ConcurrentLinkedQueue的初始状态如上图所示,即队列为空。单线程添加元素,此时,添加元素10,则状态如下所示
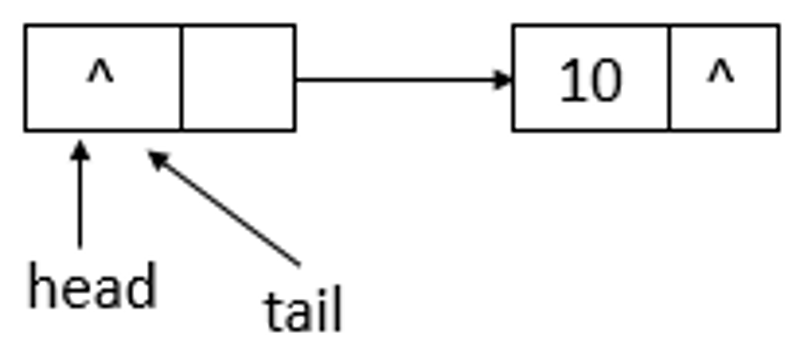
如上图所示,添加元素10后,tail没有变化,还是指向之前的结点,继续添加元素20,则状态如下所示
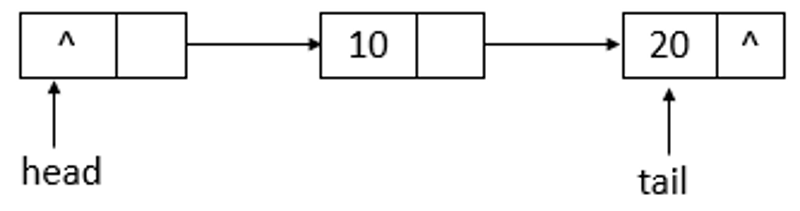
如上图所示,添加元素20后,tail指向了最新添加的结点。
poll函数
public E poll() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) { // 无限循环
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) { // 保存头结点
// item项
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) { // item不为null并且比较并替换item成功
// Successful CAS is the linearization point
// for item to be removed from this queue.
if (p != h) // p不等于h // hop two nodes at a time
// 更新头结点
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
// 返回item
return item;
}
else if ((q = p.next) == null) { // q结点为null
// 更新头结点
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
else if (p == q) // p等于q
// 继续循环
continue restartFromHead;
else
// p赋值为q
p = q;
}
}
}说明: 此函数用于获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回null。下面模拟poll函数的操作,队列状态的变化(假设单线程操作,状态为之前offer10、20后的状态,poll两次)。

队列初始状态如上图所示,在poll操作后,队列的状态如下图所示
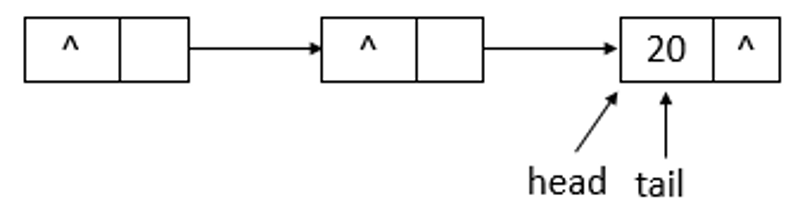
如上图可知,poll操作后,head改变了,并且head所指向的结点的item变为了null。再进行一次poll操作,队列的状态如下图所示。

如上图可知,poll操作后,head结点没有变化,只是指示的结点的item域变成了null。
remove函数
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 元素为null,返回
if (o == null) return false;
Node<E> pred = null;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) { // 获取第一个存活的结点
// 第一个存活结点的item值
E item = p.item;
if (item != null &&
o.equals(item) &&
p.casItem(item, null)) { // 找到item相等的结点,并且将该结点的item设置为null
// p的后继结点
Node<E> next = succ(p);
if (pred != null && next != null) // pred不为null并且next不为null
// 比较并替换next域
pred.casNext(p, next);
return true;
}
// pred赋值为p
pred = p;
}
return false;
}说明: 此函数用于从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。其中,会调用到first函数和succ函数,first函数的源码如下
Node<E> first() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) { // 无限循环,确保成功
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
// p结点的item域是否为null
boolean hasItem = (p.item != null);
if (hasItem || (q = p.next) == null) { // item不为null或者next域为null
// 更新头结点
updateHead(h, p);
// 返回结点
return hasItem ? p : null;
}
else if (p == q) // p等于q
// 继续从头结点开始
continue restartFromHead;
else
// p赋值为q
p = q;
}
}
}说明: first函数用于找到链表中第一个存活的结点。succ函数源码如下
final Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {
// p结点的next域
Node<E> next = p.next;
// 如果next域为自身,则返回头结点,否则,返回next
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}说明: succ用于获取结点的下一个结点。如果结点的next域指向自身,则返回head头结点,否则,返回next结点。下面模拟remove函数的操作,队列状态的变化(假设单线程操作,状态为之前offer10、20后的状态,执行remove(10)、remove(20)操作)。

如上图所示,为ConcurrentLinkedQueue的初始状态,remove(10)后的状态如下图所示
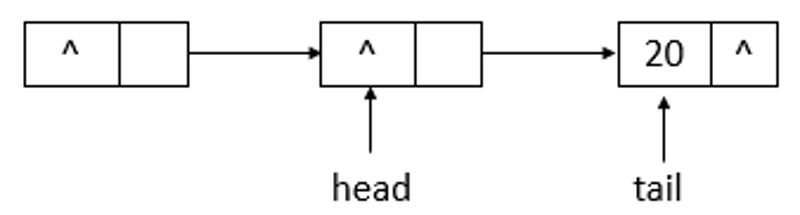
如上图所示,当执行remove(10)后,head指向了head结点之前指向的结点的下一个结点,并且head结点的item域置为null。继续执行remove(20),状态如下图所示
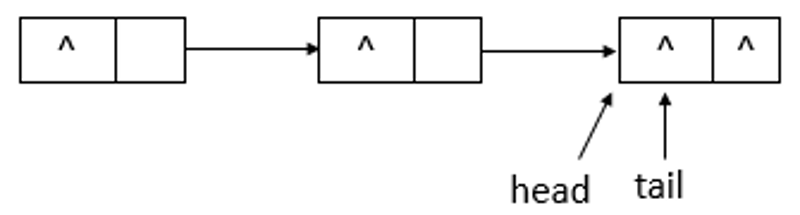
如上图所示,执行remove(20)后,head与tail指向同一个结点,item域为null。
size函数
public int size() {
// 计数
int count = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) // 从第一个存活的结点开始往后遍历
if (p.item != null) // 结点的item域不为null
// Collection.size() spec says to max out
if (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE) // 增加计数,若达到最大值,则跳出循环
break;
// 返回大小
return count;
}说明: 此函数用于返回ConcurrenLinkedQueue的大小,从第一个存活的结点(first)开始,往后遍历链表,当结点的item域不为null时,增加计数,之后返回大小。